Kia Sportage: Cylinder Block: Repair procedures
Kia Sportage: Cylinder Block: Repair procedures
Third generation SL (2010ŌĆō2016) / Kia Sportage SL Service & Repair Manual / Engine Mechanical System / Cylinder Block / Cylinder Block: Repair procedures
| Disassembly |
|
|
In case of removing the high pressure fuel pump, high
pressure fuel pipe, delivery pipe, and injector, there may be injury
caused by leakage of the high pressure fuel. So donŌĆÖt do any repair
work right after engine stops. |
| 1. |
Remove the engine assembly from the vehicle. (Refer to Engine and transaxle assembly in this group) |
| 2. |
Install the engine to an engine stand for disassembly. |
| 3. |
Remove the intake manifold and exhaust manifold. (Refer to Intake and exhaust system in this group) |
| 4. |
Remove the timing chain. (Refer to Timing system in this group) |
| 5. |
Remove the cylinder head assembly. (Refer to Cylinder head in this group) |
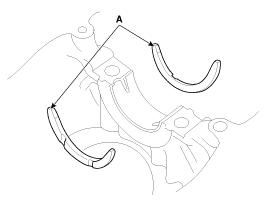
| 6. |
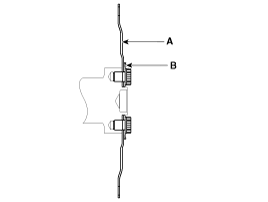
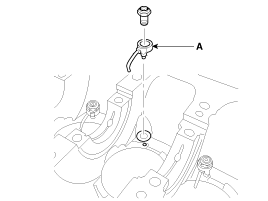
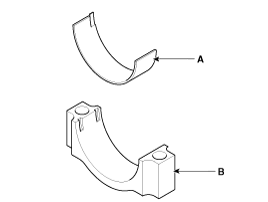
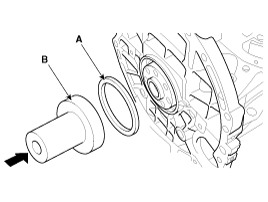
Remove the drive plate (A) and the adapter plate (B).
|
| 7. |
Remove the balance shaft & oil pump assembly. (Refer to Lubrication system in this group) |
| 8. |
Remove the A/C compressor. (Refer to HA group) |
| 9. |
Remove the alternator. (Refer to EE group) |
| 10. |
Remove the water pump assembly. (Refer to Cooling system in this group) |
| 11. |
Remove the tensioner assembly integrated bracket (A).
|
| 12. |
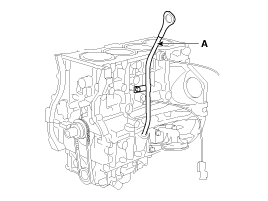
Remove the oil level gauge tube (A).
|
| 13. |
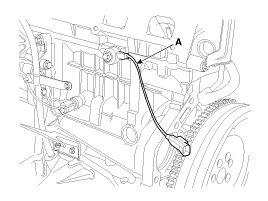
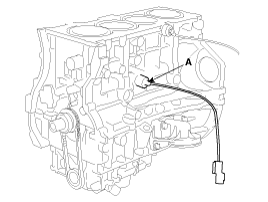
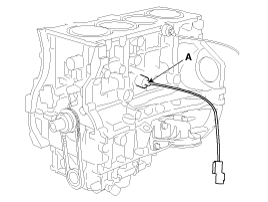
Remove the knock sensor (A).
|
| 14. |
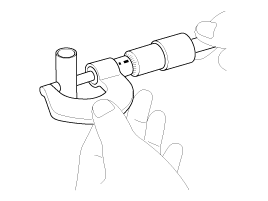
Remove the oil pressure sensor (A).
|
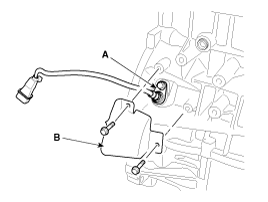
| 15. |
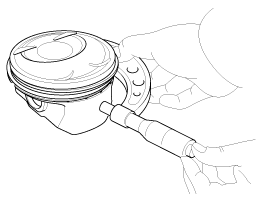
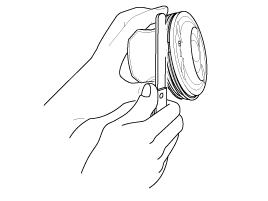
Remove the cover (B) and then CKPS (Crankshaft position sensor) (A).
|
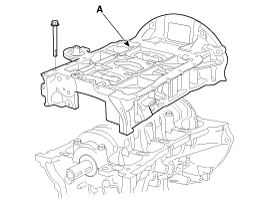
| 16. |
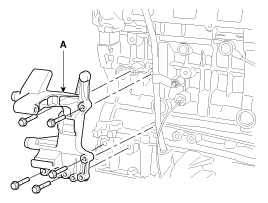
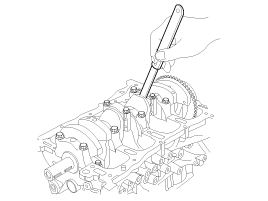
Remove the ladder frame (A).
|
| 17. |
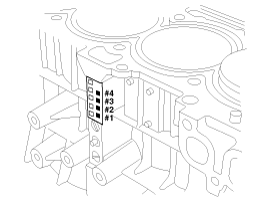
Check the connecting rod end play. |
| 18. |
Remove the connecting rod caps and check oil clearance. |
| 19. |
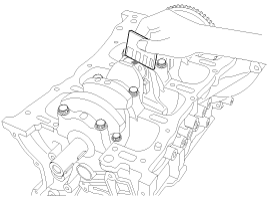
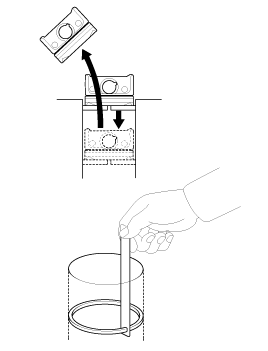
Remove piston and connecting rod assemblies.
|
| 20. |
Remove crankshaft bearing cap and check oil clearance. |
| 21. |
Check the crankshaft end play. |
| 22. |
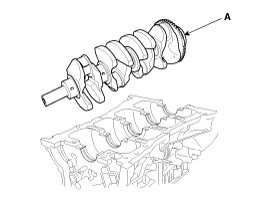
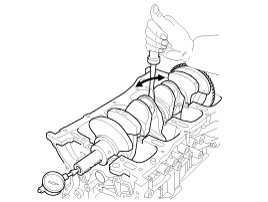
Lift the crankshaft (A) out of the engine, being careful not to damage journals.
|
| 23. |
Remove the oil jet (A).
|
| 24. |
Check fit between piston and piston pin.
Try to move the piston back and forth on the piston pin. If any movement is felt, replace the piston and pin as a set. |
| 25. |
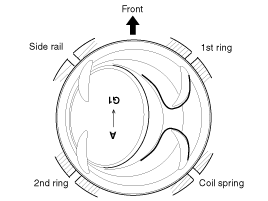
Remove piston rings.
|
| 26. |
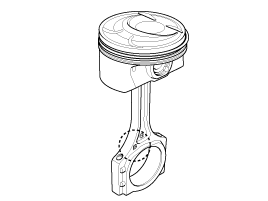
Disconnect connecting rod from piston.
Remove the snap ring at both ends of piston pin. And push the piston pin to seperate and connecting rod |
| Inspection |
Connecting Rod
| 1. |
Check the connecting rod end play.
Using a feeler gauge, measure the end play while moving the connecting rod back and forth.
|
| 2. |
Check the connecting road bearing oil clearance.
|
| 3. |
Inspect the connecting rods.
|
Crankshaft
| 1. |
Check the crankshaft bearing oil clearance.
Crankshaft Bore Identification Mark
Letters have been stamped on the block as a mark for the size of each of the 5 main journal bores.
Use them, and the numbers or bar stamped on the crank (marks for main journal size), to choose the correct bearings.
Cylinder Block Specifications
Crankshaft Journal Identification Mark
Crankshaft Specifications
Crankshaft Bearing Identification Mark
Crankshaft Bearing Specifications
Selection Chart For Crankshaft Bearings
|
| 2. |
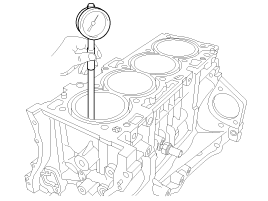
Check crankshaft end play.
Using a dial indicator, measure the thrust clearance while prying the crankshaft back and forth with a screwdriver.
If the end play is greater than maximum, replace the thrust bearings as a set.
|
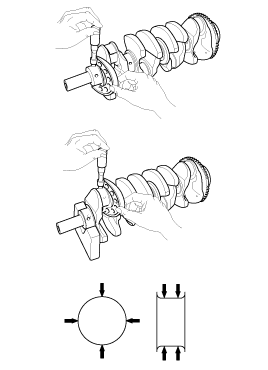
| 3. |
Inspect main journals and crank pins.
Using a micrometer, measure the diameter of each main journal and crank pin.
|
Cylinder Block
| 1. |
Remove gasket material.
Using a gasket scraper, remove all the gasket material from the top surface of the cylinder block. |
| 2. |
Clean cylinder block
Using a soft brush and solvent, thoroughly clean the cylinder block. |
| 3. |
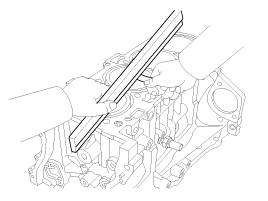
Inspect top surface of cylinder block for flatness.
Using a precision straight edge and feeler gauge, measure the surface contacting the cylinder head gasket for warpage.
|
| 4. |
Inspect cylinder bore diameter.
Visually check the cylinder for vertical scratchs.
If deep scratches are present, replace the cylinder block. |
| 5. |
Inspect cylinder bore diameter.
Using a cylinder bore gauge, measure the cylinder bore diameter at position in the thrust and axial directions.
|
| 6. |
Check the cylinder bore size code on the cylinder block.
Cylinder Bore Inner Diameter
|
| 7. |
Check the piston size code on the piston top face.
Piston Outer Diameter
|
| 8. |
Select the piston related to cylinder bore class.
|
Piston And Rings
| 1. |
Clean piston
|
| 2. |
The standard measurement of the piston outside diameter is taken 17mm (0.67in.) from the top land of the piston.
|
| 3. |
Calculate the difference between the cylinder bore diameter and the piston diameter.
|
| 4. |
Inspect the piston ring side clearance.
Using a feeler gauge, measure the clearance between new piston ring and the wall of the ring groove.
If the clearance is greater than maximum, replace the piston. |
| 5. |
Inspect piston ring end gap.
To measure the piston ring end gap, insert a piston ring into
the cylinder bore. Position the ring at right angles to the cylinder
wall by gently pressing it down with a piston. Measure the gap with a
feeler gauge. If the gap exceeds the service limit, replace the piston
ring. If the gap is too large, recheck the cylinder bore diameter
against the wear limits, If the bore is over the service limit, the
cylinder block must be replaced.
|
Piston Pins
| 1. |
Measure the diameter of the piston pin.
|
| 2. |
Measure the piston pin-to-piston clearance.
|
| 3. |
Check the difference between the piston pin diameter and the connecting rod small end diameter.
|
| Reassembly |
|
| 1. |
Assemble the piston and connecting rod.
|
| 2. |
Install the piston rings.
|
| 3. |
Install the connecting rod bearings.
|
| 4. |
Install the main bearings.
|
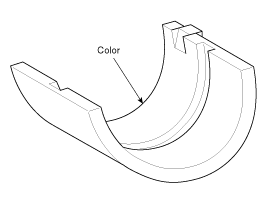
| 5. |
Install the thrust bearings.
Install the 2 thrust bearings(A) under the No.3 journal position of the cylinder block with the oil grooves facing outward.
|
| 6. |
Install the oil jet (A).
|
| 7. |
Place the crankshaft(A) on the cylinder block.
|
| 8. |
Place the main bearing caps on cylinder block. |
| 9. |
Install the main bearing cap bolts.
|
| 10. |
Check crankshaft end play. |
| 11. |
Install piston and connecting rod assemblies.
|
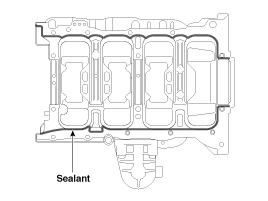
| 12. |
Apply liquid gasket to the mating surface of cylinder block and ladder frame.
|
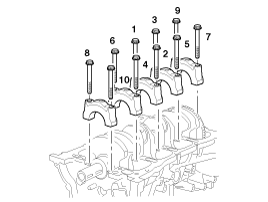
| 13. |
Install ladder frame(A) with 10 bolts, in several passes, in sequence shown.
|
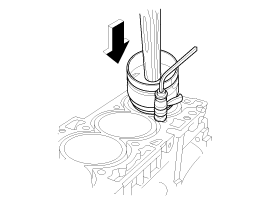
| 14. |
Install rear oil seal.
|
| 15. |
Install CKPS (Crankshaft position sensor) (A) and sensor cover (B).
|
| 16. |
Install oil pressure switch.
|
| 17. |
Install knock sensor(A).
|
| 18. |
Install oil level gauge assembly.
|
| 19. |
Install tensioner assembly integrated bracket(A).
|
| 20. |
Install the water pump. (Refer to Cooling system in this group) |
| 21. |
Install the alternator. (Refer to EE group) |
| 22. |
Install the balance shaft & oil pump assembly. (Refer to Lubrication system in this group) |
| 23. |
Install the cylinder head assembly. (Refer to Cylinder head in this group) |
| 24. |
Install the timing chain. (Refer to Timing system in this group) |
| 25. |
Install the intake manifold and exhaust manifold.
(Refer to Intake and exhaust system in this group) |
| 26. |
Remove the engine from the engine stand. |
| 27. |
Install the drive plate (A) and the adapter plate (B).
|
| 28. |
Install the engine assembly on the vehicle.
(Refer to Engine and transaxle assembly in this group)
Add all fluids to their normal operating levels. |
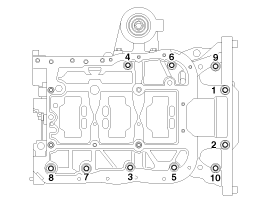
 Cylinder Block: Components and Components Location
Cylinder Block: Components and Components Location
Components
1. Piston ring2. Snap ring3. Piston4. Connecting rod 5. Connecting rod upper bearing6. Piston pin7. Connecting rod lower bearing8. Connecting rod bearing cap9. Ladder frame10. Oil filt ...
 Cooling System
Cooling System
...
Other Information:
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
SymptomSuspect AreaRemedyWater leaks from panoramaroof Deteriorated roof lid weatherstripReplaceExcessive roof lid-to-body clearance and Improperly fitted weatherstripAdjustWind n ...
35R Clutch Control Solenoid Valve(35R/C_VFS): Repair procedures
Inspection
1.
Turn ignition switch OFF.
2.
Remove the air duct (A).
3.
Remove the air cleaner assembly.
(1)
Disconnect the breather hose (A) and brake booster intensifier hose.
(2)
...
Categories
- Home
- Kia Sportage QL (2015-2019) Owners Manual
- Kia Sportage QL (2015-2019) Service Manual
- Kia Sportage SL 2010-2016 Owners Manual
- Kia Sportage SL 2010-2016 Service Manual
Copyright ® www.kispmanual.com 2014-2026